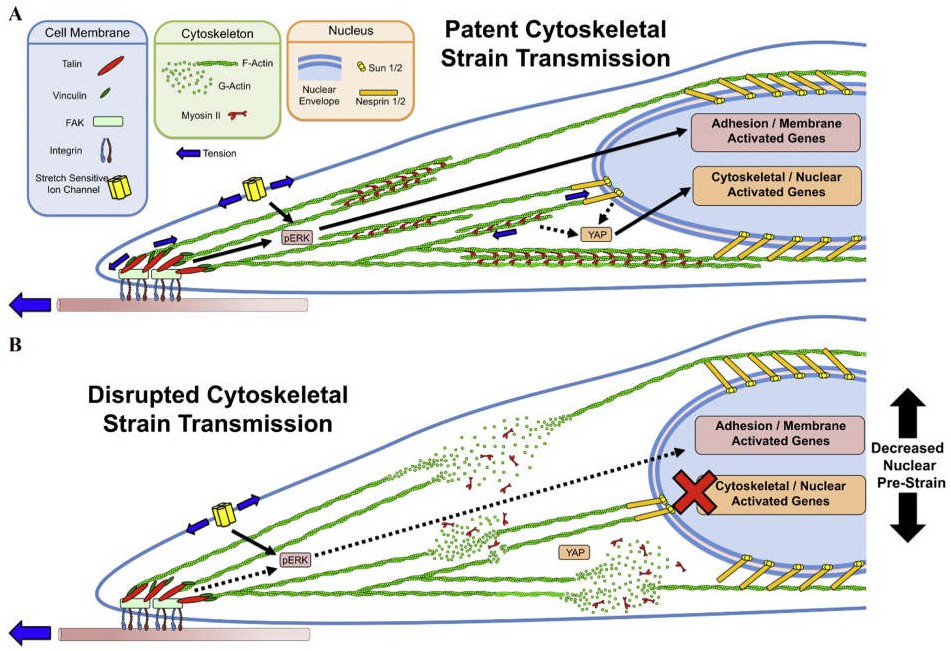
Fig. 13. Schematic illustration of the different routes of mechanotransduction from the cell surface to cell nuclear. Mechanoactivation may induce via cell membrane-mediated mechanotransduction elements or through cytoskeletal/nuclear strain transfer-mediated mechanotransduction elements. (A) Under basic conditions, both routes are probably operational. (B) By inhibiting ROCK, a decrease in nuclear prestrain and actin depolymerization has occurred; when the level of Nespirin 1/2 decreases, the transfer of cytoskeletal strain to the nucleus is also compromised. This leads to a loss in the cytoskeletal-to-nuclear strain transfer that is necessary for YAP nuclear localization and activation (Reprinted with permission, Cell Press, for citation see [118]).